selected item
Energy and environment
Unconventional resource development
Learn about the resources, technology and processes involved in unconventional resource development.
What are unconventional resources?
In unconventional oil and natural gas development, the oil and gas is found in low permeability reservoirs.
Learn more
Technology and process

Phases of natural gas production
Before any wells are drilled, extensive surveillance is done to study the locations of the underground natural gas reservoir and the nature of the local topography, so as to ensure minimal impact of operations on the local community.
Article

Horizontal drilling
Article
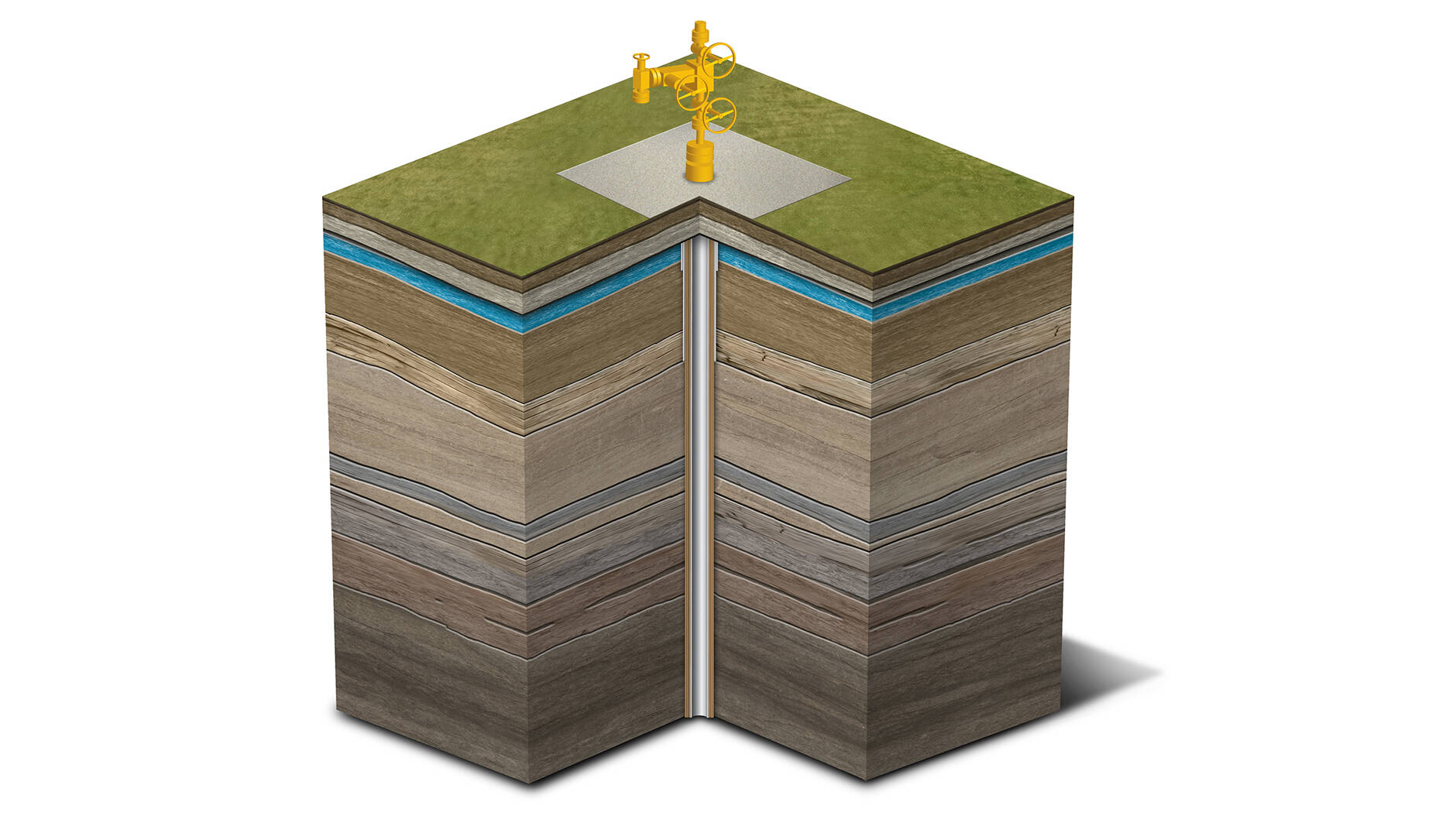
Well construction and integrity
A properly designed and constructed oil and gas well is essential to protecting the water table and ensuring successful production.
Article

Unconventional resource development
Learn about the resources, technology and processes involved in unconventional resource development.
Topic
Equipment
Natural gas extraction and production requires a mix of resources and equipment. The geographical diversity of those supplying the equipment needed to bring unconventional supplies of oil and natural gas to the surface shows the far-flung nature of fracking manufacturing and its economic benefits.
Learn more Benefits of natural gas and oil
Natural gas offers reliable, flexible power generation with significantly reduced CO₂ emissions at a competitive price, making it a long-term solution to meeting the world’s future energy needs.
Learn more


